The Corneal Pachymetre performs the corneal pachymetry. The corneal pachymetry is an examination which measures the thickness of the cornea. The central thickness of the cornea is an important indicator for the estimation of glaucoma. Eyes with a corneal thickness of 550 μm or less are three times more likely to develop glaucoma from eyes with a corneal thickness greater than 590 μm.

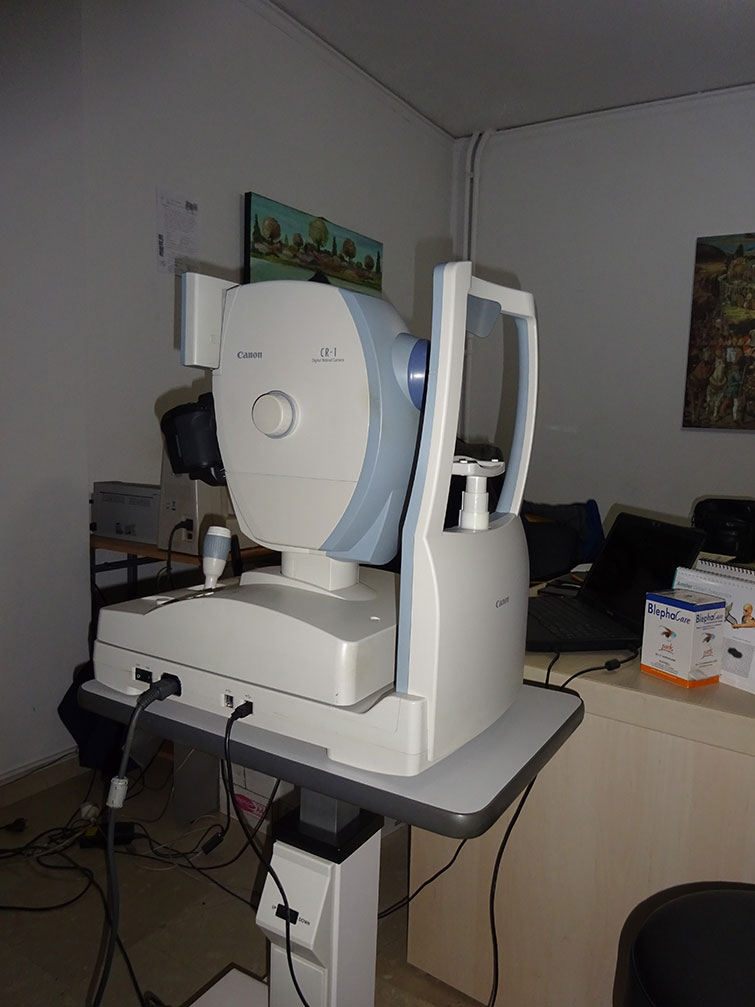
Τhe Fundus Camera without Mydriasis (dilation of the pupil) performs the fundoscopy through eye fundus photography. Fundoscopy is the examination of eye fundus, i.e. the examination of the retina and the vitreous in order to promptly diagnose those eye diseases involving the interior of the eye.
Τhe Air-Puff Tonometre performs the tonometry. Tonometry is a very important examination that checks the pressure in the eye (intraocular pressure), i.e. it determines the pressure of the aqueous humour inside the eye to find if it is within normal limits.
Τhe Air-Puff Tonometre is based on air puff, which measures the eye resistance when a constant amount of air applies on it.
The intraocular pressure above normal limits leads to glaucoma, which, if not treated early, can lead to blindness, causing irreversible damage to the optic nerve.

| CORNEA THICKNESS μm | INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE mmHg |
| 445 | 14 |
| 455 | 15 |
| 465 | 15 |
| 475 | 16 |
| 485 | 17 |
| 495 | 17 |
| 505 | 18 |
| 515 | 19 |
| 525 | 20 |
| 535 | 20 |
| 545 | 21 |
| 555 | 22 |
| 565 | 22 |
| 575 | 23 |
| 585 | 24 |
| 595 | 25 |
| 605 | 25 |
| 615 | 26 |
| 625 | 27 |
| 635 | 27 |
| 645 | 28 |
The Retinoscope performs the retinoscopy. Retinoscopy is an eye examination that constitutes the safest way of determining the refractive problem of a child or a young person in general. Children and young people have great adaptive capacity, so providing glasses is not safe unless we temporarily remove it. Retinoscopy is therefore intended to precisely determine the refractive error to the objective extent possible, so that the glasses to be given are not wrong.
The visual fields perform the optical perimetry. The optical perimetry is the most widespread examination of the functionality of the optic nerve. The examination is based on identifying a number of light stimuli of various dimensions, which are appropriately displayed by the diagnostic system. The examination of the visual fields is directly related to the diagnosis and monitoring of glaucoma, but also to the investigation of neurological diseases. The examination estimates the central vision and mainly the peripheral vision.
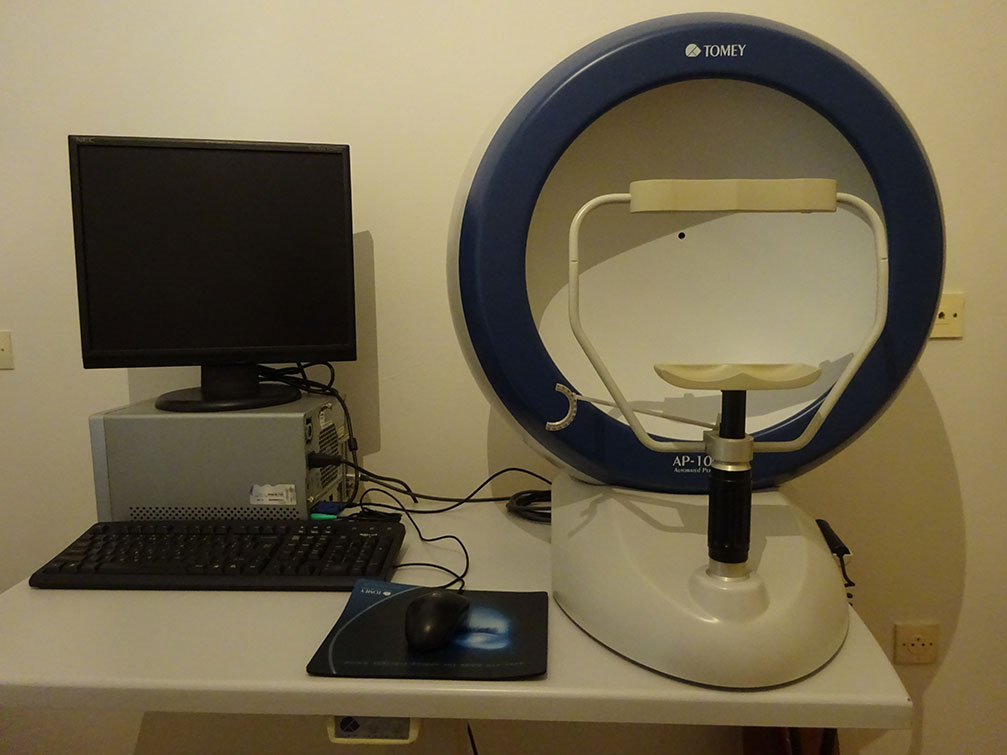
The Keratometre-Refractometre performs the keratometry and refractometry. The keratometry is used to measure the diametre and curvature of the cornea in order to diagnose cases with keratoconus, but also to determine the diametre of contact lenses. The refractometry measures the refractive anomalies of the eyes (myopia, hypermetropia and astigmatism).
The visual acuity is quantitatively measured by controlling the smallest object that the examined person can distinguish at a given distance with the best refractive correction (myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism). It is a measure of the sharpness of our vision. The ophthalmologist evaluates it by asking us to read from a wall diagram until the letters become very small, up to 10/10.
During the slit lamp examination, a slit light beam of a specific microscope is focused in the eye. In that way the ophthalmologist can see in detail the cornea, the pupil, the crystalline lens and the vitreous body of our eye..
Instrument for measuring spectacle lenses.